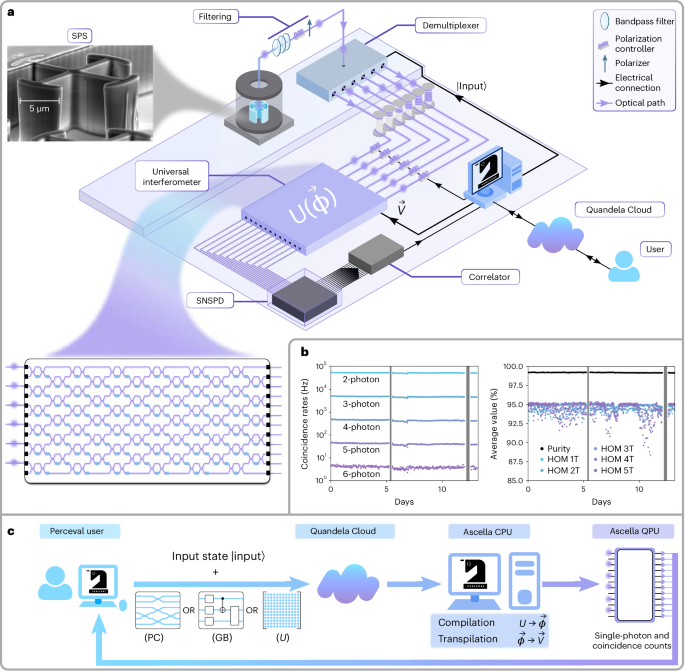
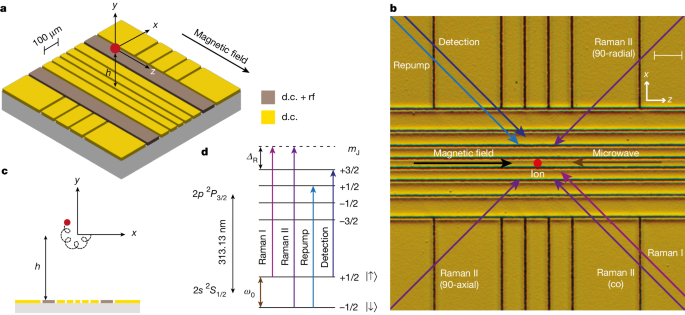
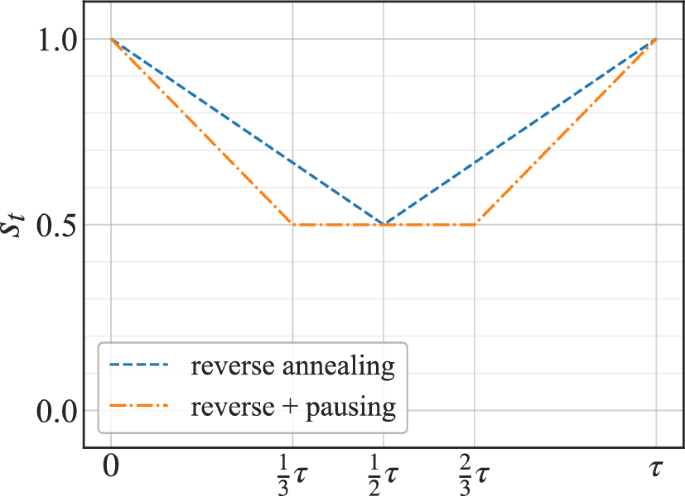
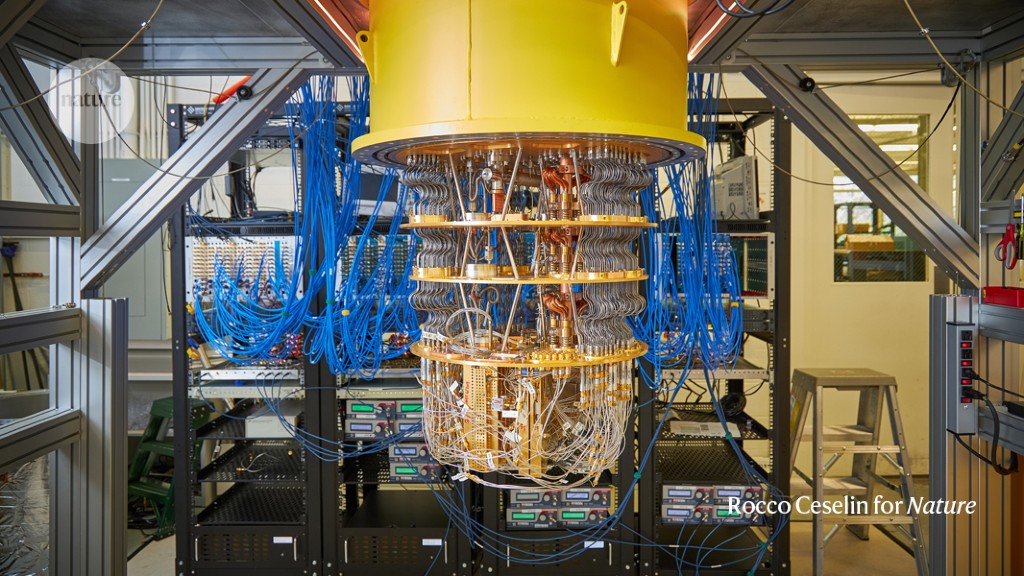
A versatile single-photon-based quantum computing platform
Arute, F. et al. Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505–510 (2019). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zhu, Q. et al. Quantum computational advantage via 60-qubit 24-cycle random circuit sampling. Sci. Bull. 67, 240–245 (2022). Article Google Scholar Moses, S. A. et al. A race-track trapped-ion quantum processor. Phys. Rev. X …