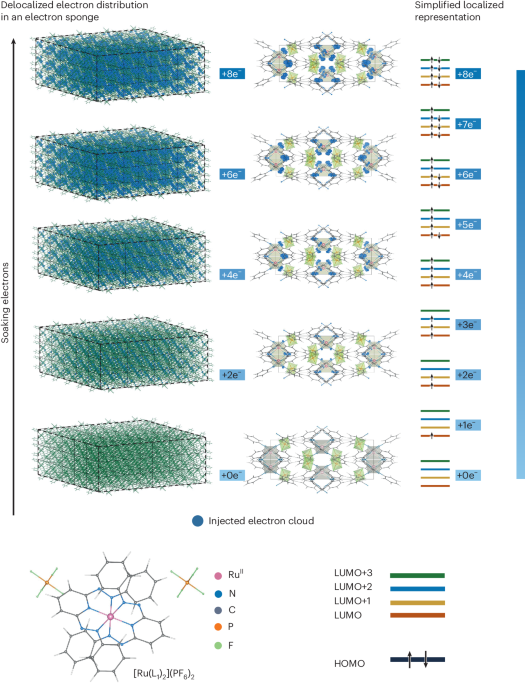
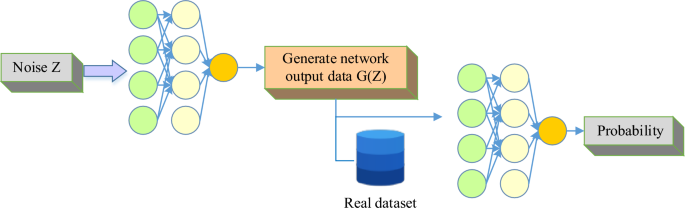
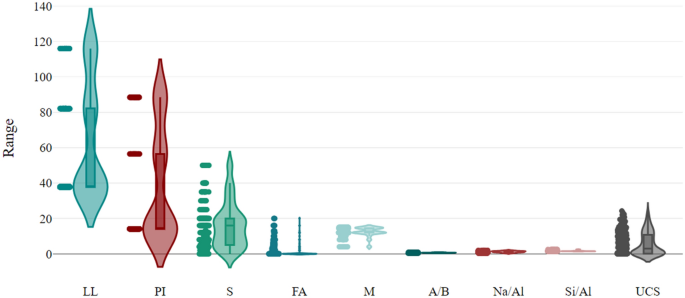
Topological Phonons Discovered in Crystal Lattices
An international research team has shown that phonons, the quantum particles behind material vibrations, can be classified using topology, much like electronic bands in materials. This breakthrough could lead to the development of new materials with unique thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties, enhancing our understanding and manipulation of solid-state physics. Researchers from an international consortium …