
Looking ahead, the convergence of MEC with emerging technologies like AI and IoT heralds a new frontier in computing. As businesses and service providers navigate these challenges, the adoption of MEC is poised to redefine connectivity, pushing the boundaries of digital innovation.
Imagine the convenience of having a coffee shop right next to your home, ensuring your coffee remains piping hot upon arrival. This scenario mirrors the principle behind Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), a transformative approach that brings data processing and cloud services closer to the data source, akin to a nearby coffee shop. MEC stands as a pivotal advancement in our hyper-connected era, mitigating latency and bandwidth issues by processing vast data volumes near their origin.
The burgeoning investment in MEC by telecom service providers, anticipated to surge from USD 5.4 billion in 2022 to USD 11.6 billion in 2027 by STL Partners, underscores its growing significance. This investment facilitates the provision of edge computing services such as low-latency gaming and seamless video streaming, heralding a new era of digital interaction.
Unlocking the power of MEC
MEC’s architecture is distinguished by several key features:
- Proximity: By processing data close to its source, MEC drastically reduces the need to send data across long distances, enhancing efficiency.
- Real-time processing: It caters to applications requiring immediate data processing, offering near-instantaneous decision-making capabilities.
- Low latency: With latency under 20 milliseconds, MEC significantly enhances user experiences and responsiveness.
- Autonomous operations: MEC applications can operate independently, ensuring continuous service even when disconnected from the central network.
- Interoperability and virtualization: MEC simplifies app development and deployment, supporting seamless integration with existing cloud resources.
Navigating the MEC ecosystem
MEC’s ecosystem comprises three fundamental components:
- MEC Host: The hardware layer, offering essential networking, storage, and processing power. It’s strategically positioned near end-users to facilitate swift data processing.
- MEC Platform: Acting as a bridge, the platform enables efficient communication between applications and the host, leveraging APIs for resource accessibility.
- MEC Applications: These applications exploit the host’s resources to deliver services with minimal latency, catering to a wide array of use cases from IoT to augmented reality.
See also: AI on the Edge: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source
Top 10 trends reshaping multi-edge computing in 2024
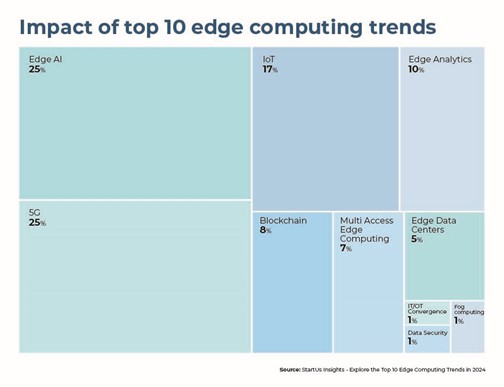

- Edge AI: AI at the edge addresses the challenge of managing vast data volumes with algorithms to reduce latency and bandwidth, enabling real-time processing. EDGENeural.ai offers an end-to-end platform for deploying AI models on hardware efficiently, focusing on high accuracy and speed.
- 5G: Enhancing edge computing with faster, low-latency connections, 5G facilitates quicker real-time communication. Rapid.Space’s open 5G edge cloud infrastructure supports private 4G/5G networks, reducing operational costs and supporting IoT and mobility integration.
- IoT: Facilitating robust device connectivity, IoT simplifies edge data collection and promotes intelligent system responses. Venius’ IoT platform for smart offices utilizes edge analytics and ML for efficient data management and analysis.
- Edge Analytics: Processing data locally with advanced analytics techniques, edge analytics enables immediate insights without the latency of data transmission. Blockalytics’ federated industrial analytics for IoT applications offers decentralized insight extraction, enhancing data ownership and reducing costs.
- Blockchain: Ensuring data integrity and security in edge environments, blockchain technology provides a secure framework for data transactions. Atkrypto.io’s decentralized ledger technology secures edge and IoT data, facilitating peer-to-peer blockchains and asset tokenization.
- Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC): By moving cloud resources closer to edge devices, MEC accelerates data processing and access to cloud services. Nife Labs’ platform simplifies the deployment of applications across 5G and edge environments, enhancing privacy and reducing costs.
- Edge data centers: Bringing data processing closer to the source, edge data centers allow for distributed computing and storage. Edge Centres’ solar-powered facilities offer sustainable, secure, and low-latency computing resources globally.
- IT/OT convergence: Integrating operational and information technologies enhances data sharing and system efficiency. Perygee’s cybersecurity platform secures IT/OT devices, simplifying compliance and enhancing organizational security.
- Data security: Protecting edge data from breaches and unauthorized access, data security measures ensure data integrity. Primary Guard’s edge cybersecurity solutions guard against attacks and preserve critical operations with advanced DDoS protection and endpoint security.
- Fog computing: Extending the edge with decentralized processing, fog computing enhances scalability and reduces bandwidth needs. Datasance’s Edge Intelligence Platform leverages fog computing for real-time data analysis and decision-making at the edge layer.
Critical growth catalysts for MEC in 2024
Emerging trends and adoption
A notable shift is underway, with more than 50% of large enterprises set to deploy at least six edge computing use cases by the end of 2023, a dramatic increase from less than 1% in 2019. Furthermore, 57% of mobility leaders are incorporating edge computing into their 2024 roadmaps, propelled by the growth of OTT media streaming, the rollout of 5G, and widespread IoT adoption across industries.
OTT video streaming enhancement
The OTT user base is expected to reach 3.71 billion by 2024, growing by nearly 300 million from 2023. This surge demands telecom infrastructure upgrades to manage the increased video traffic and ensure quality user experiences. MEC optimizes network infrastructure to support new video applications, enhancing video service quality by reducing latency and improving bandwidth efficiency.
Synergy between 5G and MEC
Predictions indicate that by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed at the network edge, thanks to the adoption of 5G. The convergence of edge computing and 5G technologies enhances application performance and facilitates real-time data analysis. This synergy offers several benefits, including network virtualization, extended reach, reduced latency, and improved reliability and security.
MEC’s evolution is tightly interwoven with the advancement of mobile networks, notably 5G, marking a significant leap in enabling a multitude of new services and applications. From connected vehicles to augmented reality, MEC enriches user experiences by providing faster, more reliable access to data and services.
The integration of 5G amplifies MEC’s capabilities, offering unprecedented speeds and bandwidth essential for data-intensive applications. This combination is pivotal for developing applications that require real-time processing, from enhancing public safety systems with real-time surveillance to enabling autonomous vehicle communication.
Advanced deployment strategies in edge computing
Strategic deployment considerations – The growing interest in edge computing opens new avenues for enhancing user experiences. However, leveraging this technology effectively requires strategic planning to avoid common pitfalls and maximize benefits.
Adopting open standards – To avoid vendor lock-in and ensure flexibility, businesses should utilize open standards for developing edge applications. Open standards like WebAssembly and HTTP enable seamless transitions between platforms and vendors, offering the agility needed for future growth.
Serverless architecture advantages – Serverless architecture has gained popularity for its scalability and efficiency, allowing developers to focus on application innovation without backend concerns. Utilizing pre-made templates and analytics directly from the edge, developers can rapidly deploy and evaluate edge applications.
Actionable observability – Utilizing the edge for real-time troubleshooting and observability is crucial for maintaining optimal application performance. Real-time performance metrics from edge deployments provide immediate insights, facilitating proactive problem resolution and enhancing user personalization.
Securing the edge – Integrating security features into edge applications is essential for protecting against cyber threats. Early detection and perimeter defense strategies can mitigate potential attacks, ensuring a secure edge environment.
Balancing edge and cloud processing – Deciding between edge and cloud processing depends on the specific needs of the application. While edge computing is ideal for fast, localized processing, cloud computing is necessary for handling large-scale data aggregation and analysis.
Transformative cross-industry MEC use cases
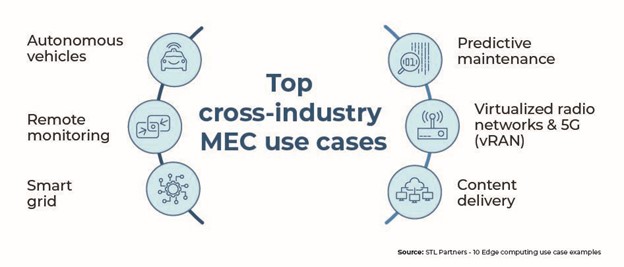

- Autonomous vehicle convoys: Enhancing efficiency on the road: One of the pioneering applications in autonomous transportation is the automated platooning of trucks. This technique allows a convoy of trucks to drive in close formation, significantly reducing air drag, conserving fuel, and alleviating road congestion. Edge computing plays a crucial role here, enabling real-time communication between the trucks (except the lead vehicle) with minimal latency, thereby eliminating the need for human drivers.
- Remote monitoring: Safeguarding critical infrastructure: In the oil and gas sector, where asset malfunctions can lead to dire consequences, continuous monitoring is essential. Often located in remote areas, these facilities benefit from edge computing’s ability to bring real-time analytics closer to the point of data generation. This reduces reliance on high-quality, continuous cloud connectivity, ensuring operational integrity even in the most isolated locations.
- Smart grids: Revolutionizing energy management: Edge computing is set to become a cornerstone in the widespread adoption of smart grids, enabling businesses to optimize their energy usage efficiently. Through sensors and IoT devices connected to an edge network, energy consumption is monitored in real time, paving the way for more sustainable and efficient energy management practices.
- Predictive maintenance: Proactive problem-solving in manufacturing: To prevent downtimes, manufacturers deploy edge computing solutions that bring data processing and storage closer to the machinery. IoT sensors monitor equipment health with negligible delays, facilitating real-time analytics that predict and prevent potential failures before they disrupt production lines.
- Virtualized Radio Networks and 5G (vRAN): A new era for telecom: Telecommunications operators are increasingly moving towards virtualizing portions of their mobile networks through vRAN for its cost savings and flexibility advantages. This shift requires sophisticated processing capabilities at lower latencies, necessitating the deployment of edge servers close to cell towers to support the burgeoning demands of 5G technology.
- Enhanced content delivery: Streamlining digital experiences: Content delivery networks (CDNs) are evolving, with a push to cache content—ranging from videos and music to web pages—directly at the network’s edge. This strategy drastically reduces latency and enhances user experiences. As content providers extend their CDN footprints to the edge, they achieve greater network flexibility and customization, dynamically adapting to fluctuations in user traffic and demands.
Challenges and considerations in edge computing
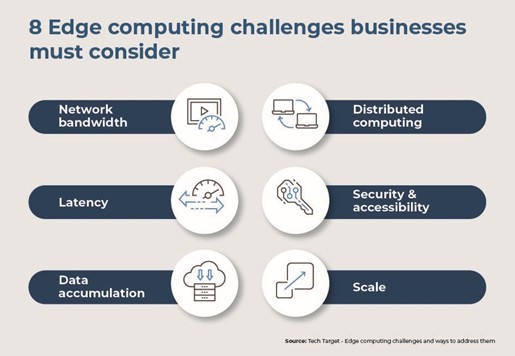

Network bandwidth: As data processing shifts to the network edge, the demand for higher network bandwidth escalates, necessitating scalable network solutions to accommodate edge computing’s data throughput needs.
Latency reduction: Edge computing significantly reduces application latency by situating computation closer to data sources. This dual-core and edge placement strategy enhances data exchange and access management but requires careful coordination across the network.
Data management: Edge data collection introduces complex legal and operational challenges, emphasizing the need for stringent data handling standards to mitigate risks and ensure compliance during data access and storage processes.
Distributed computing: The shift towards edge computing demands attention to edge locations as integral elements of computing use cases. This evolution towards distributed models highlights the increasing importance of networking as a fundamental aspect of computation due to the rise in east-west traffic.
Security and accessibility: Edge computing transforms security protocols by requiring remote servers to maintain robust physical and network security measures. With the edge environment’s diverse device access points, IT teams must meticulously define access permissions to safeguard data integrity.
Scaling challenges: The proliferation of devices connected at the edge amplifies scaling demands, challenging IT teams to adapt their strategies for deploying applications efficiently at the network edge.
Wrapping it up
Looking ahead, the convergence of MEC with emerging technologies like AI and IoT heralds a new frontier in computing. As businesses and service providers navigate these challenges, the adoption of MEC is poised to redefine connectivity, pushing the boundaries of digital innovation.

Wanda Parisien is a computing expert who navigates the vast landscape of hardware and software. With a focus on computer technology, software development, and industry trends, Wanda delivers informative content, tutorials, and analyses to keep readers updated on the latest in the world of computing.



