In a breakthrough discovery, the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) satellite mission, a collaboration between NASA and the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ), has revealed that after years of severe drought and declining groundwater levels, California has experienced its highest year-over-year water gains in two decades. The state’s water deficit, accumulated during the past decade including the driest years on record, has been partially alleviated by the abundance of atmospheric rivers during this winter.
The Central Valley region of California can be visualized as a massive swimming pool. The GRACE-FO satellite mission takes into account the water contained in lakes, rivers, soil, snowpack, and underground aquifers within this area. Between October 2022 and March 2023, the storms added enough water to raise the water level in this “swimming pool” by approximately 20 inches (500 millimeters). This amount is twice the average winter water gain since GRACE-based water storage measurements began in 2002.
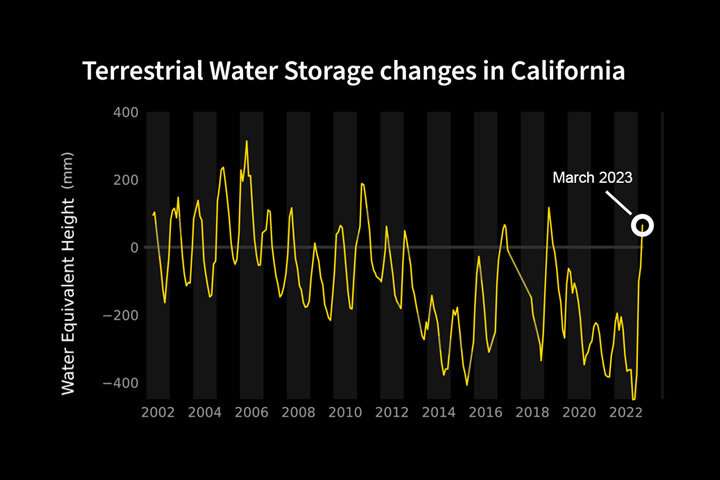
The maps above clearly illustrate the rise in water between October 2022 and March 2023. Blue represents wetter-than-average conditions compared to the period from 2004 to 2010, while red indicates drier-than-average conditions. The yellow line in the chart below demonstrates the month-to-month variations in water storage for the region outlined in yellow on the maps.
While surface water basins are refilling, it may take years for underground fresh water reserves (aquifers) to fully recharge. Felix Landerer, the GRACE-FO project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, cautioned that one good winter of rain and snow cannot compensate for years of extreme drought and extensive use of groundwater. The GRACE-FO team will closely monitor the evolution of California’s water storage throughout the summer, once the snowpack melts and water levels in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs begin to decrease during drier weather.
The remarkable observations were made possible by the unique sensing approach employed by both GRACE missions. As water moves around in various forms such as ocean currents, falling rain, shifting groundwater, and ice, it alters the Earth’s mass near the surface, thereby slightly changing Earth’s gravitational pull. GRACE-FO precisely measures these subtle changes, allowing scientists to estimate shifts in the total water volume in a given area.
Similar to its predecessor, the GRACE-FO mission involves two identical satellites flying one behind the other. As the leading satellite passes over an area with greater mass, such as a region with more water compared to another, the slight change in gravity pulls it forward, increasing the distance between the two satellites. The spacecraft’s microwave and laser instruments accurately measure these minute changes in distance, providing insights into the overall mass of water responsible for these alterations.
Denial of responsibility! TechCodex is an automatic aggregator of the all world’s media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, and all materials to their authors. For any complaint, please reach us at – [email protected]. We will take necessary action within 24 hours.

Jessica Irvine is a tech enthusiast specializing in gadgets. From smart home devices to cutting-edge electronics, Jessica explores the world of consumer tech, offering readers comprehensive reviews, hands-on experiences, and expert insights into the coolest and most innovative gadgets on the market.


